What kind of global disaster on the Internet will the BGP route leak cause?
Recently, I was studying the global catastrophe accident on the Internet. I suddenly saw this latest accident and felt very enlightening, so I share it with everyone.
Cause and effect
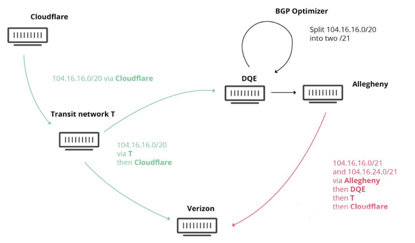
On June 24, 2019, a telecommunications operator in Pennsylvania named "DQE (AS33154)".
The company learned BGP global routing from AT & T and optimized it using the BGP optimizer. The so-called optimization is to extend the network mask bit of the route to make the route more detailed.
For example, 104.20.0.0/20, after optimization, becomes two routes, one is 104.20.0.0/21 and the other is 104.20.8.0/21.
If the optimized route is only used in its own AS, there is no problem at all, but it must not be advertised through BGP.
Routing rules
According to the "longest match" routing rule of the route, 104.20.0.0/21 or 104.20.8.0/21 is definitely better than 104.20.0.0/20, so the traffic on the Internet accessing "104.20.0.0/20" will pass DQE Transit.
Unfortunately, DQE sent these optimized routes to its neighbor Allegheny, and then Allegheny these optimized routes spread into the global routing table.
Disaster strikes
Cloudflare accesses the "104.16.16.x" traffic to the first hop ATT. The ATT router matches the longest match and matches the "104.16.16.0/21" route to the DQE, so the traffic is sent to the DQE.
DQE received the packet to query the routing table, and matched the optimized route "104.16.16.0/21", and found that the next hop was still the ATT router, so it sent the traffic to the ATT router.
The ATT router then sends it to the DQE router, and a three-layer loop is formed.
Every time the TTL in the IP packet is processed by the router minus 1, the initial value of TTL = 255. After 255 loops, it is finally discarded.
However, the continuous flow of traffic on the network is rushing forward, and within a few seconds, the routers of DQE and ATT are crushed by massive traffic, and Internet services are partially interrupted. . .
The above is just an example. All routes optimized by the BGP optimizer are affected by this.
If several "ifs" are allowed
If 1: DQE does not use BGP route optimizer, this disaster will not occur
If 2: Do not advertise optimized routes to BGP neighbors, but advertise the original routes to neighbors
If 3: The receiver checks the validity of the route and rejects the optimized route
If 4: Or for the received route, query the authoritative mapping (official signature) of the route and AS number online. Any mapping that is not queried will be rejected.
Then, this disaster will not happen!
This incident was caused by humans, but it is not a malicious attack, it may be caused by the mistake of the engineer.
But from this incident, it can be seen that a small mistake can completely ruin the Internet, which is by no means alarmist.
Internet insecurity
The Internet is very fragile and depends on the work of BGP. In the past 20 years, in order to provide BGP security, it has generally focused on the protection of BGP packets, such as using pre-shared passwords to authenticate neighbors, using shared keys to verify the HMAC of packets, and using TTL = 1 to mitigate remote attacks.
When I saw this event, I deeply felt the importance of digital signatures in route distribution, which can repel any intentional or unintentional BGP route injection, because any illegal injection route will be rejected and discarded by the receiver, thus making global routing The routing entries in the table are trustworthy. Through correct and legal route navigation, you can navigate IP packets to the real destination!
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps and CCNP Written dumps waiting for you.
Comments
Post a Comment