LACP technology explained
In short, Link Aggregation technology is to aggregate multiple physical links into a logical link with a higher bandwidth. The bandwidth of the logical link is equal to the sum of the bandwidth of the aggregated multiple physical links.
The number of aggregated physical links can be configured according to the bandwidth requirements of the service. Therefore, link aggregation has the advantages of low cost and flexible configuration. In addition, link aggregation also has the function of link redundancy backup, and the aggregated links dynamically backup each other, which improves the stability of the network.
There was no uniform standard for the realization of early link aggregation technology. Each manufacturer had its own proprietary solutions, which were not completely the same in function and incompatible with each other.
Therefore, the IEEE has specially formulated a standard for link aggregation. The current official standard for link aggregation technology is IEEE Standard 802.3ad, and Link Aggregation Control Protocol is one of the main contents of the standard, which is a protocol for dynamic link aggregation. .
After the LACP protocol of a port is enabled, the port will advertise its system priority, system MAC address, port priority, port number, and operation key to the peer by sending LACPDU.
After receiving the information, the opposite end compares the information with the information stored in other ports to select a port that can be aggregated, so that both parties can reach an agreement on the port joining or leaving a dynamic aggregation group.
The operation key is a configuration combination generated by the LACP protocol according to the port configuration (that is, speed, duplex, basic configuration, and management key) during port aggregation.
After the LACP protocol is enabled for the dynamic aggregation port, its management key defaults to zero. After LACP is enabled for a static aggregation port, the management key of the port is the same as the aggregation group ID.
For a dynamic aggregation group, members of the same group must have the same operation key, while in the manual and static aggregation groups, the active port has the same operation key.
Port aggregation is the aggregation of multiple ports together to form an aggregation group, so as to realize the load sharing among the member ports in the aggregation group, and also provide higher connection reliability.
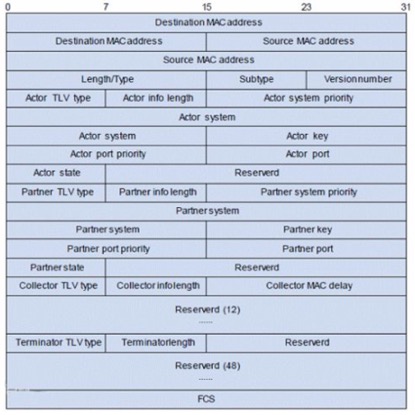
Introduction to the main fields:
Actor_Port/Partner_Port: local/peer interface information.
Actor_State/Partner_State: Local/Partner State.
Actor_System_Priority/Partner_System_Priority: local/peer system priority.
Actor_System/Partner_System: Local/Peer system ID.
Actor_Key/Partner_Key: Local/peer operation key, the same value of each interface can be aggregated.
Actor_Port_Priority/Partner_Port_Priority: local/peer interface priority.
Overview of static and dynamic LACP:
Static lacp aggregation is manually configured by the user, and the system is not allowed to automatically add or delete ports in the aggregation group. The aggregation group must contain at least one port.
When there is only one port in the aggregation group, the port can only be deleted from the aggregation group by deleting the aggregation group. The LACP protocol of the static aggregation port is active. When a static aggregation group is deleted, its member ports will form one or more dynamic LACP aggregations and keep the LACP activated. Users are forbidden to close the lacp protocol of the static aggregation port.
Dynamic lacp aggregation is an aggregation created/deleted automatically by the system, and users are not allowed to add or delete member ports in the dynamic lacp aggregation.
Only ports that have the same rate and duplex properties, are connected to the same device, and have the same basic configuration can be dynamically aggregated. Even if there is only one port, a dynamic aggregation can be created. At this time, it is a single-port aggregation. In dynamic aggregation, the lacp protocol of the port is enabled.
Port status in static aggregation group:
In a static aggregation group, the port may be in two states: selected or standby.
Both the selected port and the standby port can send and receive the lacp protocol, but the standby port cannot forward user messages.
In a static aggregation group, the system sets the port in the selected or standby state according to the following principles:
The system selects the port with the highest priority in the selected state according to the priority order of port full duplex/high rate, full duplex/low rate, half duplex/high rate, half duplex/low rate, and other ports are in standby state .
It is different from the peer device connected to the smallest port in the selected state, or the port connected to the same peer device but the port is in a different aggregation group will be in the standby state.
Ports cannot be aggregated together due to hardware limitations (cannot be aggregated across boards), and ports that cannot aggregate with the smallest port in the selected state will be in the standby state.
Ports that are different from the basic configuration of the smallest port in the selected state will be in the standby state.
Since the number of selected ports in the aggregation group that the device can support is limited, if the current number of member ports exceeds the maximum number of selected ports that the device can support, the system will select some ports as selected ports in the order of port numbers from small to large , The others are standby ports.
Port status of dynamic aggregation group:
In a dynamic aggregation group, the port may be in two states: selected or standby. Both the selected port and the standby port can send and receive the lacp protocol, but the standby port cannot forward user messages.
Since the maximum number of ports in the aggregation group that the device can support is limited, if the current number of member ports exceeds the maximum number of ports, the local system and the peer system will negotiate, based on the port with the best device id. The size of the id determines the status of the port.
The specific negotiation steps are as follows:
Compare the device id (system priority + system mac address). First compare the system priority, if the same, then compare the system mac address. The end with the smaller device id is considered superior.
Compare port id (port priority + port number). For each port on the end with the best device ID, the port priority is first compared, and if the priority is the same, the port number is compared. The port with the smaller port id is the selected port, and the remaining ports are standby ports.
In an aggregation group, the port with the smallest port number in the selected state is the main port of the aggregation group, and the other ports in the selected state are the member ports of the aggregation group.
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps, CCNP Written dumps and CCIE Written dumps waiting for you.
Comments
Post a Comment