Latest EIGRP protocol notes
Today we will review and self-check the brief description of the EIGRP protocol DUAL dispersion update algorithm.
Diffusing Update Algorithm, or diffusion update algorithm, is one of the EIGRP components and provides the best routing path for EIGRP. DUAL is a method for EIGRP to determine the best loop-free path and loop-free backup path.
We must first understand these terms:
1) easydistance, FD: refers to the smallest metric for the router to reach the destination network.
2) reporteddistance, RD: the feasible distance from the EIGRP neighbor to the same destination network. The reporting distance is a measure of the cost that the router reports to its neighbors about its own access to the network.
3) easycondition, FC: When the reported distance (RD) of the neighbor to a network is shorter than the feasible distance from the local router to the same destination network, the feasible condition (FC) is met.
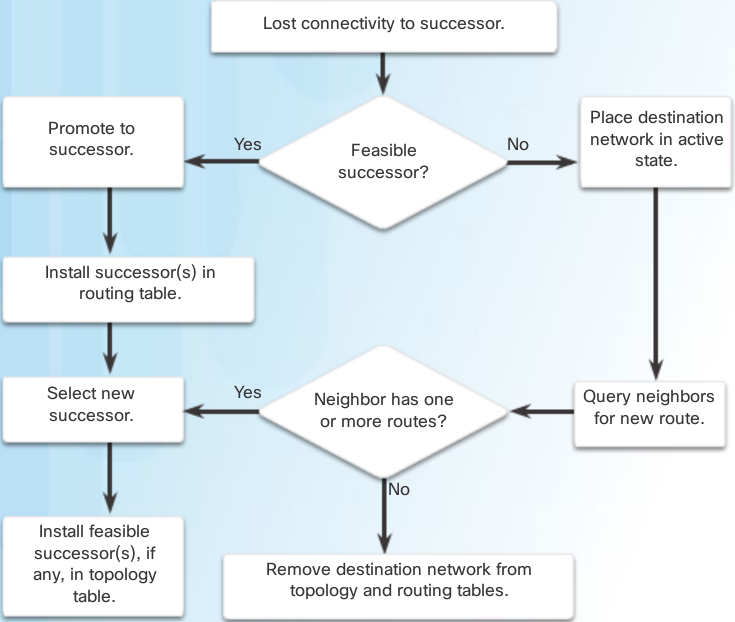
4) Successor: The neighboring router that meets the feasible conditions and has the shortest distance to the destination network is the next-hop router.
5) easysuccessor: A feasible successor router (FS) refers to a neighbor. It has a loop-free backup path to the same destination network to which the successor router is connected, and meets the feasibility conditions. (To become a viable successor router, the feasibility condition (FC) must be met). The feasible successor router also reduces the number of diffusion calculations and improves network performance.
The key to its rapid convergence is twofold:
The EIGRP router maintains a copy of all neighbors’ routes. Using this copy, they can calculate the cost of reaching the remote network. If the best path is not available, it simply tests the contents of the topology table and selects the best. Alternative routes;
When there are no alternative routes in its local topology table, EIGRP routers will quickly ask neighbors for help. They are not afraid to seek guidance! Dependence on other routers and the use of the information they provide are the characteristics of DUAL, which is the "dispersion" feature.
DUAL algorithm summary:
1. Record all routes advertised to me by neighbors and write to the topology table.
2. Select the one with the smallest FD to be the successor and write it into the IP routing table.
3. According to the principle that the route AD is less than the optimal route FD, select a feasible successor.
4. If the optimal route fails, check the topology table. If there is a feasible successor, you can directly use it as a new optimal route (the route remains in the Passive state); if there is no feasible successor, query the route from all EIGRP neighbors (the route becomes Active).
DUAL finite state machine: When a certain event occurs, the DUAL algorithm will be recalculated; DUAL and DUAL's EIGRP routing calculation engine are the core content of EIGRP. The exact name of this technology is DUAL finite state machine. The finite state machine contains all the logic for calculating and comparing routes in the EIGRP network.
DUAL:
The difference between DUAL and SPF algorithm:
The OSPF protocol was developed in the late 1980s and became an industry standard in the early 1990s. It is a typical link-state protocol. The main features of OSPF include: support for VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask), rapid convergence, and low bandwidth occupancy.
The OSPF protocol exchanges link state information between neighbors, so that after the router establishes the link state database (LSDB), the router uses the SPF (Shortest Path First, shortest path first) algorithm to calculate the routing table according to the information in the database, and selects the main path. The basis is bandwidth.
EIGRP is an enhanced version of IGRP, which is also Cisco's proprietary routing protocol. EIGRP uses the DUAL update algorithm. To a certain extent, it is similar to the distance vector algorithm, but has a shorter convergence time and better operability. As an extension to IGRP, EIGRP supports a variety of routable protocols, such as IP, IPX, and AppleTalk. When running in an IP environment, EIGRP can also make a smooth connection with IGRP because their measurement methods are consistent.
They are usually used inside autonomous systems. When connecting between autonomous systems, they often use inter-domain routing protocols such as BGP (Border Gateway Protocols) and EGP (External Gateway Protocols).
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps, CCNP Written dumps and CCIE Written dumps waiting for you.
Comments
Post a Comment